Webhook Routing
Webhook routing allows you to define custom conditions that route specific webhook events to different target endpoints. Instead of sending all webhooks to a single global URL, you can create multiple routes with JavaScript filter functions that determine which events should be forwarded to which destinations.
Overview
What is Webhook Routing?
EmailEngine's webhook routing system enables you to:
- Route by Account: Send webhooks for specific accounts to dedicated endpoints
- Route by Event Type: Forward only certain event types (e.g.,
messageNew) to specific handlers - Route by Content: Use JavaScript filter functions to inspect the payload and decide whether to forward
- Transform Payloads: Use mapping functions to transform the webhook payload before delivery
- Multiple Destinations: Send the same event to multiple endpoints if multiple route filters match
When to Use Webhook Routing
Multi-tenant Applications
Route webhooks for different customer accounts to separate endpoints:
// Filter: Route all webhooks for customer "acme-corp" to their dedicated endpoint
if (payload.account === 'acme-corp') {
return true;
}
Event-Specific Processing
Send different event types to specialized handlers:
// Filter: Only forward bounce notifications
if (payload.event === 'messageBounce') {
return true;
}
Reducing Webhook Volume
Filter out events you don't need to process:
// Filter: Only forward new messages in INBOX
const isInbox = payload.path === 'INBOX' || payload.data?.labels?.includes('\\Inbox');
if (payload.event === 'messageNew' && isInbox) {
return true;
}
Third-Party Integrations
Transform webhooks to match the expected format of external services like Slack, Discord, or Zapier:
// Map: Transform to Slack incoming webhook format
return {
text: `New email from ${payload.data?.from?.address}`,
blocks: [
{
type: 'section',
text: {
type: 'mrkdwn',
text: `*Subject:* ${payload.data?.subject}`
}
}
]
};
How Routing Works
Route Processing Order
When EmailEngine generates a webhook event:
- Filter Evaluation: Each enabled route's filter function is executed with the payload
- Matching Routes: All routes where the filter returns
truereceive the webhook - Payload Transformation: If a route has a mapping function, the payload is transformed before delivery
- Parallel Delivery: Webhooks are queued for delivery to all matching routes simultaneously
- Default Delivery: The webhook is also sent to either the account-specific URL or global URL (see fallback below)
Filter Function
The filter function determines whether a webhook should be sent to this route's target URL. It receives the complete webhook payload as a global variable.
Requirements:
- Must return a truthy value to forward the webhook
- Return
false,null,undefined, or any falsy value to skip - Has access to the full webhook payload via the
payloadvariable - Errors are logged but don't stop processing
Example Filter Functions:
// Forward all webhooks (default behavior)
return true;
// Forward only for specific account
if (payload.account === 'my-account-id') {
return true;
}
// Forward only new messages
if (payload.event === 'messageNew') {
return true;
}
// Forward messages from specific sender
if (payload.event === 'messageNew' &&
payload.data?.from?.address?.endsWith('@important-domain.com')) {
return true;
}
// Forward messages with specific subject pattern
if (payload.event === 'messageNew' &&
/urgent|critical/i.test(payload.data?.subject || '')) {
return true;
}
Mapping Function
The mapping function transforms the webhook payload before delivery. This is useful when integrating with third-party services that expect a specific payload format.
Requirements:
- Must return the transformed payload object
- The returned value is sent as the webhook body
- Has access to the original payload via the
payloadvariable - If not defined, the original payload is sent unchanged
Example Mapping Functions:
// Return payload unchanged (default behavior)
return payload;
// Add timestamp
payload.timestamp = Date.now();
return payload;
// Transform to Slack format
return {
text: `New email received`,
blocks: [
{
type: 'section',
text: {
type: 'mrkdwn',
text: `*From:* ${payload.data?.from?.address}\n*Subject:* ${payload.data?.subject}`
}
}
]
};
// Transform to Discord webhook format
return {
content: `New email from ${payload.data?.from?.name || payload.data?.from?.address}`,
embeds: [
{
title: payload.data?.subject,
description: payload.data?.text?.plain?.substring(0, 200) || '',
color: 5814783
}
]
};
// Simplify payload for processing
return {
event: payload.event,
account: payload.account,
messageId: payload.data?.id,
from: payload.data?.from?.address,
subject: payload.data?.subject,
receivedAt: payload.date
};
Disabling the Default Webhook
When using webhook routing, you may want to disable the default global webhook to avoid receiving duplicate events. The default webhook is configured in the main webhook settings and receives all events (based on the event filter).
Understanding Webhook Hierarchy
EmailEngine processes webhooks in two parallel tracks:
Track 1: Webhook Routes (Independent)
Custom webhook routes are always evaluated first and independently. If a route's filter function returns true, the webhook is sent to that route's target URL. Multiple routes can match the same event, each receiving their own copy.
Track 2: Default Webhook Delivery (Fallback Chain)
After routes are processed, EmailEngine sends the webhook to a "default" destination using this fallback order:
- Account-Specific Webhook URL - If the account has a dedicated webhook URL configured, the webhook is sent there
- Global Webhook URL - If no account-specific URL is set, the global webhook URL is used
Each account can have its own dedicated webhook URL configured in the account settings. When set, this URL replaces the global webhook URL for that account - webhooks are sent to the account URL, not the global URL. This is useful for multi-tenant setups where each customer's account needs to send webhooks to their own endpoint.
Webhook routes are not affected by account-specific webhook URLs. Routes are evaluated independently and will still receive webhooks based on their filter functions, regardless of whether an account has a dedicated URL set.
To use only routed webhooks (disable both account and global default webhooks):
- Leave the global webhook URL empty, AND
- Do not set account-specific webhook URLs
To use only account-specific webhooks (no global fallback):
- Leave the global webhook URL empty
- Set webhook URLs on individual accounts as needed
Via Web UI
- Navigate to Configuration in the sidebar
- Click Webhooks
- Leave the Webhook URL field empty
- Keep Enable webhooks checked (required for routing to work)
- Click Update Settings
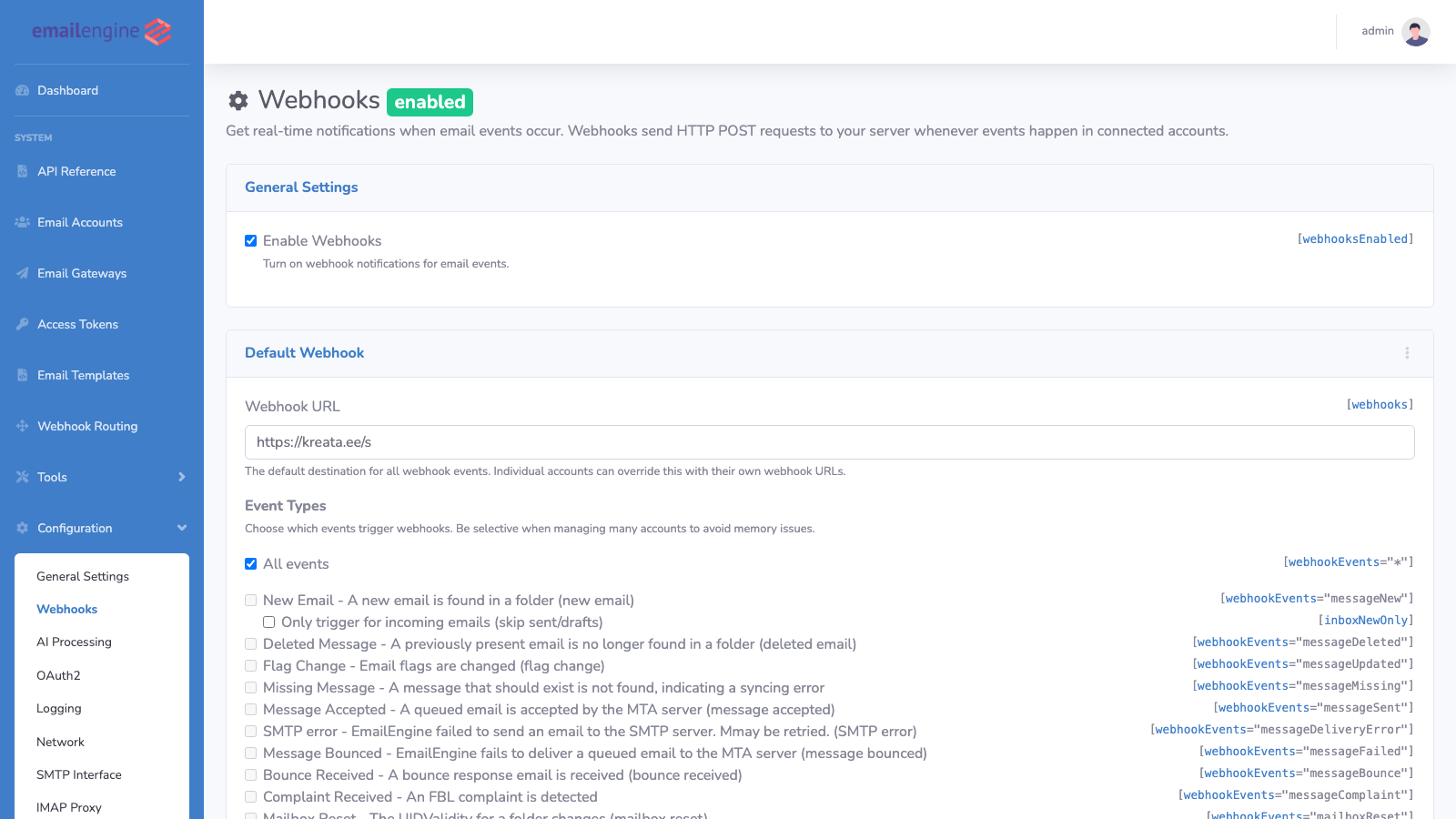
The "Enable webhooks" toggle must remain enabled for webhook routing to work. This setting controls the entire webhook system, including custom routes. Only clear the webhook URL field if you want to disable the default destination while keeping routes active.
Via API
Use the settings API to clear the default webhook URL:
- cURL
- Node.js
- Python
- PHP
curl -X POST "https://emailengine.example.com/v1/settings" \
-H "Authorization: Bearer YOUR_ACCESS_TOKEN" \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-d '{
"webhooks": "",
"webhooksEnabled": true
}'
const response = await fetch('https://emailengine.example.com/v1/settings', {
method: 'POST',
headers: {
'Authorization': 'Bearer YOUR_ACCESS_TOKEN',
'Content-Type': 'application/json'
},
body: JSON.stringify({
webhooks: '', // Empty string to disable default webhook
webhooksEnabled: true // Keep routing enabled
})
});
const result = await response.json();
console.log('Settings updated:', result.success);
import requests
response = requests.post(
'https://emailengine.example.com/v1/settings',
headers={
'Authorization': 'Bearer YOUR_ACCESS_TOKEN',
'Content-Type': 'application/json'
},
json={
'webhooks': '', # Empty string to disable default webhook
'webhooksEnabled': True # Keep routing enabled
}
)
result = response.json()
print(f"Settings updated: {result['success']}")
<?php
$ch = curl_init('https://emailengine.example.com/v1/settings');
curl_setopt_array($ch, [
CURLOPT_POST => true,
CURLOPT_RETURNTRANSFER => true,
CURLOPT_HTTPHEADER => [
'Authorization: Bearer YOUR_ACCESS_TOKEN',
'Content-Type: application/json'
],
CURLOPT_POSTFIELDS => json_encode([
'webhooks' => '', // Empty string to disable default webhook
'webhooksEnabled' => true // Keep routing enabled
])
]);
$response = curl_exec($ch);
$result = json_decode($response, true);
echo "Settings updated: " . ($result['success'] ? 'true' : 'false');
?>
Setting Account-Specific Webhook URLs
To set a dedicated webhook URL for a specific account, use the Update Account API:
- cURL
- Node.js
- Python
curl -X PUT "https://emailengine.example.com/v1/account/my-account-id" \
-H "Authorization: Bearer YOUR_ACCESS_TOKEN" \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-d '{
"webhooks": "https://customer-a.example.com/webhooks"
}'
const accountId = 'my-account-id';
const response = await fetch(`https://emailengine.example.com/v1/account/${accountId}`, {
method: 'PUT',
headers: {
'Authorization': 'Bearer YOUR_ACCESS_TOKEN',
'Content-Type': 'application/json'
},
body: JSON.stringify({
webhooks: 'https://customer-a.example.com/webhooks'
})
});
const result = await response.json();
console.log('Account updated:', result.account);
import requests
account_id = 'my-account-id'
response = requests.put(
f'https://emailengine.example.com/v1/account/{account_id}',
headers={
'Authorization': 'Bearer YOUR_ACCESS_TOKEN',
'Content-Type': 'application/json'
},
json={
'webhooks': 'https://customer-a.example.com/webhooks'
}
)
result = response.json()
print(f"Account updated: {result['account']}")
To clear an account-specific webhook URL (falling back to global webhook), set webhooks to an empty string:
curl -X PUT "https://emailengine.example.com/v1/account/my-account-id" \
-H "Authorization: Bearer YOUR_ACCESS_TOKEN" \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-d '{"webhooks": ""}'
Setting Up Routes via Web UI
Creating a New Route
- Navigate to Webhook Routing in the sidebar (under the Webhooks section)
-
Click Create new to open the route creation form
-
Fill in the route details:
- Name: A descriptive name for the route (e.g., "Notify Slack on Inbox Messages")
- Description: Optional description of what this route does
- Target URL: The webhook endpoint URL that will receive matching events
- Enable this Webhook Routing: Check to activate the route
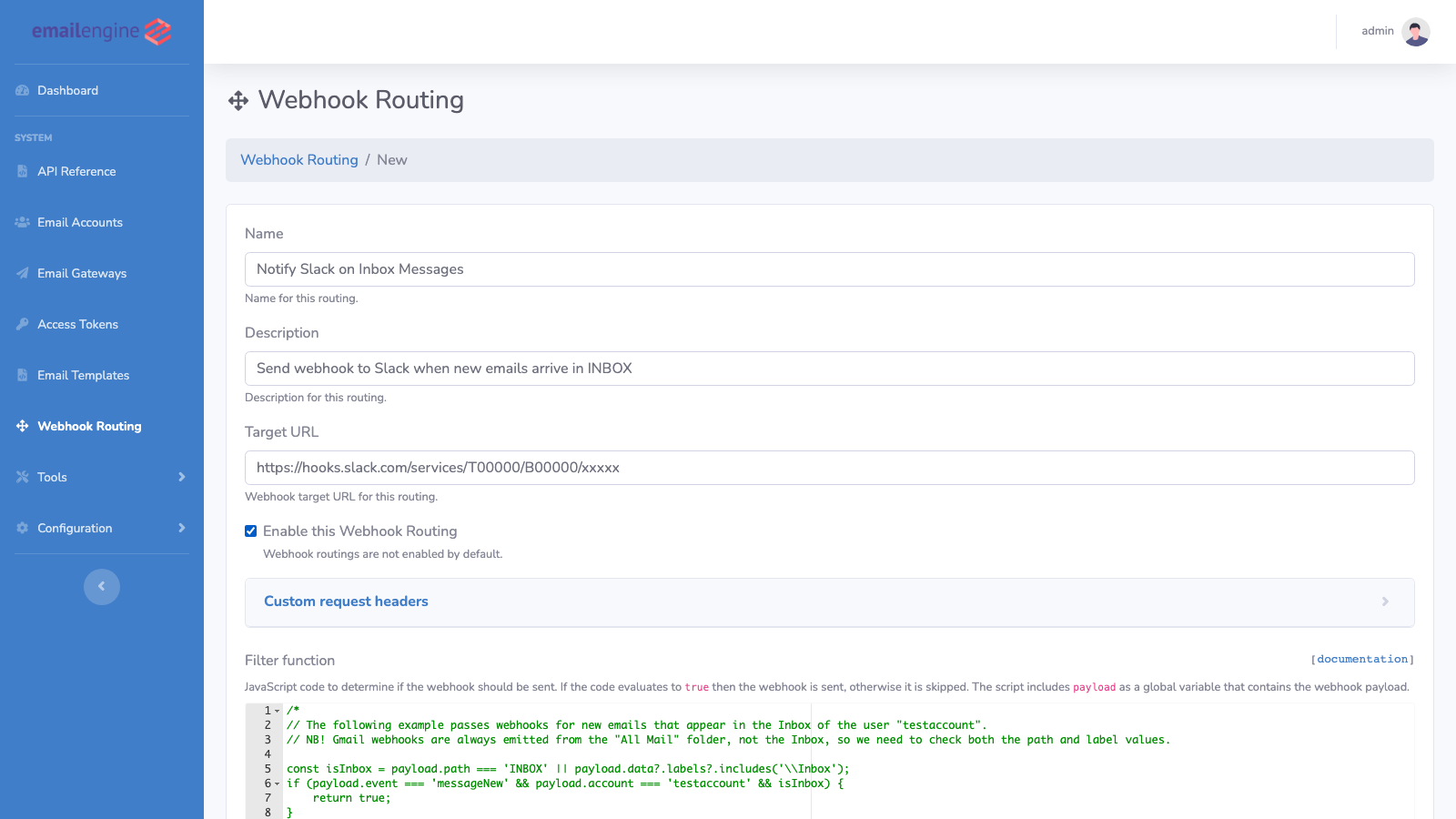
-
Configure the Filter Function:
The filter function determines which webhooks are forwarded to this route. Write JavaScript code that returns
trueto send the webhook orfalseto skip it.// Example: Only forward new messages in INBOX
const isInbox = payload.path === 'INBOX' || payload.data?.labels?.includes('\\Inbox');
if (payload.event === 'messageNew' && isInbox) {
return true;
}
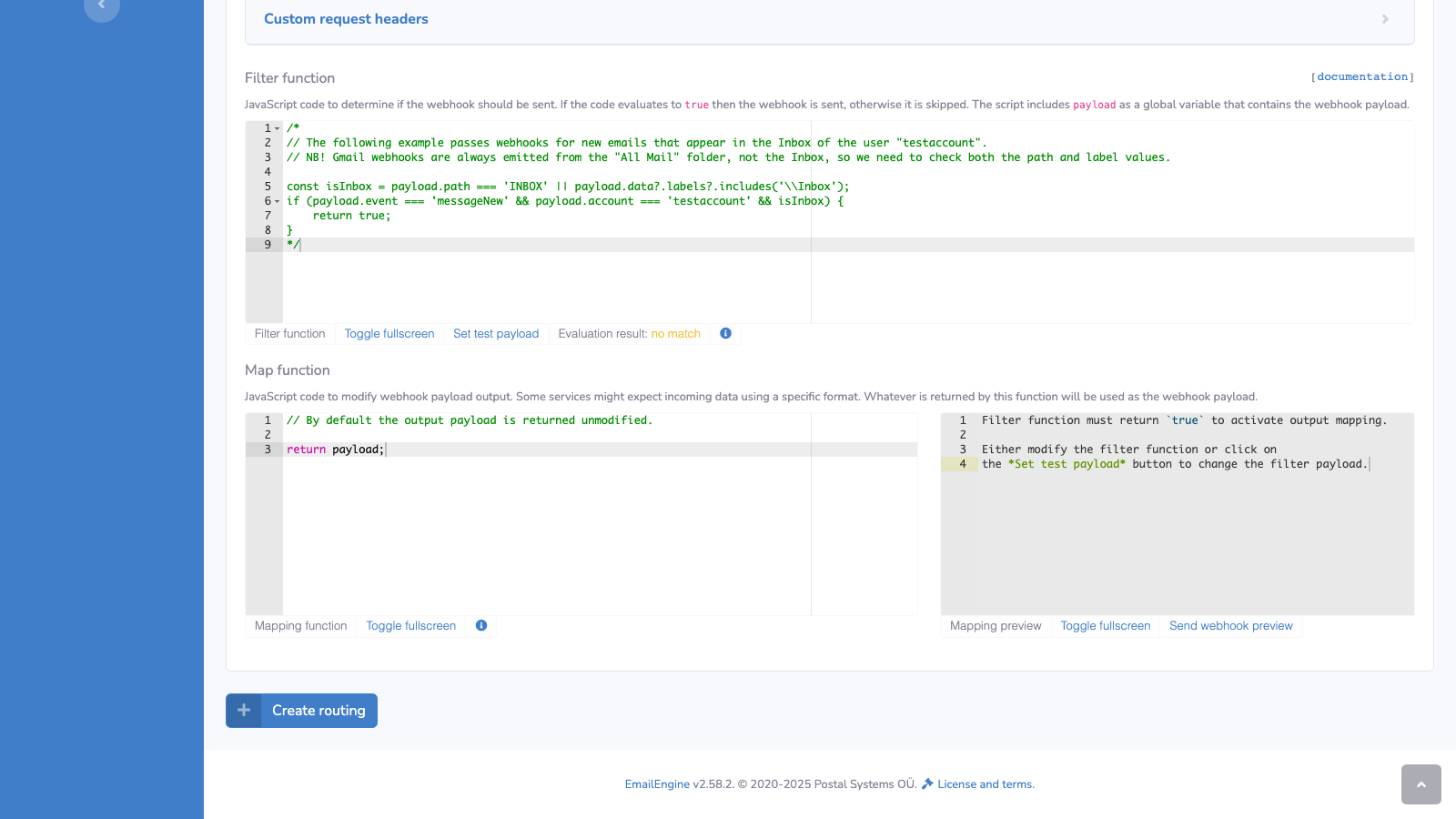
-
Configure the Map Function (optional):
The mapping function transforms the payload before sending. If not defined, the original payload is sent unchanged.
// Return payload unchanged
return payload; -
Click Create routing to save the route
Viewing Route Details
After creating a route, you can view its details including:
- Trigger count (how many times the route has been activated)
- Current status (Enabled/Disabled)
- Filter and mapping function code
- Error log (if any errors occurred during function execution)

Editing a Route
- Click on a route in the list to view its details
- Click Edit to modify the route configuration
- Make your changes and click Update routing
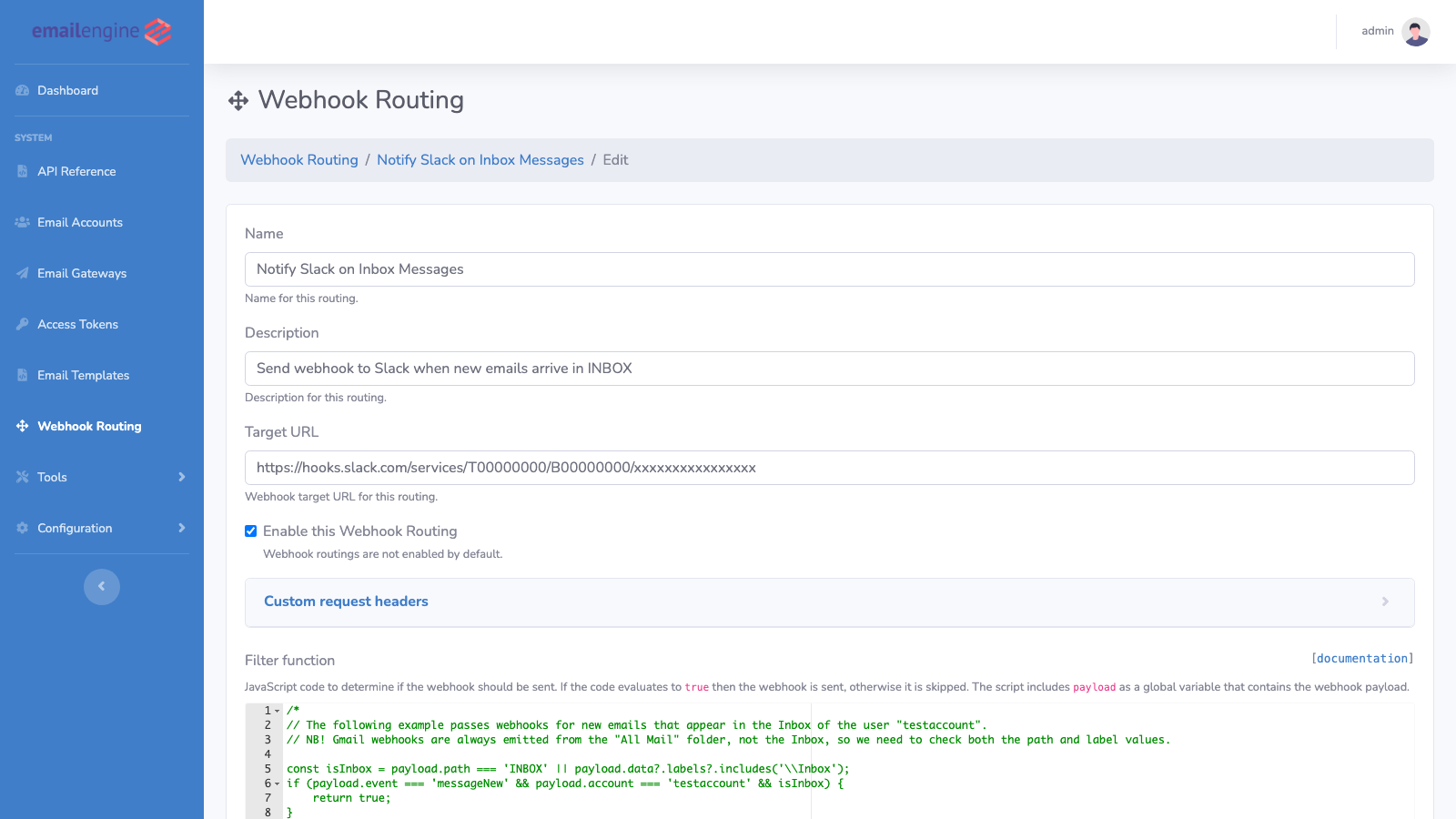
Managing Custom Headers
You can add custom HTTP headers to webhook requests for authentication or identification:
-
In the route form, expand Custom request headers
-
Add headers in
Key: Valueformat, one per line:Authorization: Bearer your-secret-token
X-Custom-Header: custom-value
Deleting a Route
- Navigate to the route detail page
- Click Delete
- Confirm the deletion in the modal dialog
Deleting a route is permanent and cannot be undone. Any webhooks that would have matched this route will no longer be delivered to its target URL.
Viewing Routes via API
You can retrieve webhook route information programmatically using the EmailEngine API:
- List routes -
GET /v1/webhookRoutes- Retrieve all configured webhook routes - Get route details -
GET /v1/webhookRoutes/webhookRoute/{webhookRoute}- Get a specific route with filter and mapping functions
Creating, updating, and deleting webhook routes is only available through the Web UI. The API provides read-only access to route information.
Practical Examples
Example 1: Route to Slack
Send new email notifications to a Slack channel with a formatted message.
Filter Function:
// Only forward new messages in INBOX
const isInbox = payload.path === 'INBOX' || payload.data?.labels?.includes('\\Inbox');
if (payload.event === 'messageNew' && isInbox) {
return true;
}
Map Function:
// Format for Slack incoming webhook
return {
text: `New email in ${payload.account}`,
blocks: [
{
type: 'header',
text: {
type: 'plain_text',
text: 'New Email Received'
}
},
{
type: 'section',
fields: [
{
type: 'mrkdwn',
text: `*From:*\n${payload.data?.from?.name || ''} <${payload.data?.from?.address}>`
},
{
type: 'mrkdwn',
text: `*Subject:*\n${payload.data?.subject || '(no subject)'}`
}
]
},
{
type: 'context',
elements: [
{
type: 'mrkdwn',
text: `Account: ${payload.account} | Received: ${new Date(payload.date).toLocaleString()}`
}
]
}
]
};
Example 2: Route by Account for Multi-Tenant
Route webhooks for different customer accounts to their dedicated endpoints.
Route 1 - Customer A:
// Filter: Only Customer A's accounts
if (payload.account.startsWith('customer-a-')) {
return true;
}
Route 2 - Customer B:
// Filter: Only Customer B's accounts
if (payload.account.startsWith('customer-b-')) {
return true;
}
Example 3: Bounce Notification Handler
Route bounce notifications to a dedicated analytics service.
Filter Function:
// Forward bounce and complaint notifications
if (payload.event === 'messageBounce' || payload.event === 'messageComplaint') {
return true;
}
Map Function:
// Simplify payload for bounce analytics
return {
type: payload.event,
account: payload.account,
originalMessageId: payload.data?.messageId,
recipient: payload.data?.recipient,
bounceType: payload.data?.bounceInfo?.action,
errorCode: payload.data?.bounceInfo?.response?.code,
errorMessage: payload.data?.bounceInfo?.response?.message,
timestamp: payload.date
};
Example 4: High-Priority Message Alert
Send immediate alerts for emails matching urgent criteria.
Filter Function:
// Check for high-priority messages
if (payload.event !== 'messageNew') {
return false;
}
const subject = (payload.data?.subject || '').toLowerCase();
const from = payload.data?.from?.address || '';
// Check priority indicators
const isUrgent = /urgent|critical|emergency|asap/i.test(subject);
const isVIP = ['ceo@company.com', 'cfo@company.com'].includes(from);
const hasHighPriority = payload.data?.headers?.['x-priority'] === '1';
if (isUrgent || isVIP || hasHighPriority) {
return true;
}
Map Function:
// Format for alerting service
return {
alertType: 'high-priority-email',
account: payload.account,
from: payload.data?.from?.address,
subject: payload.data?.subject,
preview: (payload.data?.text?.plain || '').substring(0, 200),
messageId: payload.data?.id,
receivedAt: payload.date
};
Example 5: Filter by Sender Domain
Only forward webhooks from specific sender domains.
Filter Function:
// Forward only messages from trusted domains
const trustedDomains = ['partner.com', 'supplier.com', 'client.com'];
if (payload.event === 'messageNew') {
const senderAddress = payload.data?.from?.address || '';
const senderDomain = senderAddress.split('@')[1];
if (trustedDomains.includes(senderDomain)) {
return true;
}
}
Available Variables in Functions
The payload Object
The payload variable contains the complete webhook payload. The structure varies by event type, but common fields include:
| Field | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
event | string | Event type (e.g., messageNew, messageSent) |
account | string | Account identifier |
date | string | ISO timestamp of the event |
path | string | Mailbox path (for message events) |
data | object | Event-specific data |
For messageNew events, payload.data includes:
| Field | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
id | string | EmailEngine message ID |
uid | number | IMAP UID |
messageId | string | Message-ID header value |
subject | string | Email subject |
from | object | Sender information (name, address) |
to | array | Recipients |
date | string | Message date |
labels | array | Gmail labels (if applicable) |
flags | array | IMAP flags |
text | object | Message content (plain, html) |
attachments | array | Attachment information |
See Webhook Events Reference for complete payload documentation by event type.
Additional Globals
Filter and mapping functions have access to:
| Variable | Description |
|---|---|
payload | The complete webhook payload object |
logger | Logging object with .info(), .error(), etc. |
fetch | Fetch API for making HTTP requests (async) |
URL | URL constructor for URL manipulation |
env | Environment variables defined in Script Environment settings |
The fetch function is available for making external API calls within your functions, but use it sparingly as it can slow down webhook processing. Consider using mapping functions only for payload transformation.
Troubleshooting
Route Not Triggering
Check if the route is enabled:
- Navigate to the route detail page
- Verify the status shows "Enabled"
Verify the filter function:
- Use the test payload feature in the UI to test your filter
- Check the error log tab for any JavaScript errors
- Ensure the function returns
truefor matching payloads
Confirm webhooks are enabled globally:
- Go to Configuration > Webhooks
- Ensure "Enable webhooks" is checked
Webhooks Not Being Delivered
Check the target URL:
- Verify the URL is correct and publicly accessible
- Test the URL with a simple curl request
- Check for HTTPS certificate issues
Review the webhook queue:
- Go to Tools > Bull Board
- Check the "Webhooks" queue for failed jobs
- Review error messages for delivery failures
Enable job retention:
- Go to Configuration > Service
- Set "Completed/failed queue entries to keep" to 100
- Failed webhooks will be visible in Bull Board
Filter Function Errors
Check the error log:
- Open the route detail page
- Click the "Error log" tab
- Review recent errors with their payloads
Common issues:
- Accessing undefined properties: Use optional chaining (
payload.data?.from?.address) - Syntax errors: Check for missing brackets or semicolons
- Type errors: Ensure you're comparing the right types
Mapping Function Issues
Verify the output:
- Use the mapping preview in the edit form
- Test with sample payloads
- Check that the return value is valid JSON
Common issues:
- Not returning a value: The function must return the transformed payload
- Returning undefined: Check for conditional paths that don't return
- Invalid JSON: Template strings with special characters need escaping
See Also
- Webhook Overview - General webhook concepts and setup
- Webhook Events Reference - Complete event type documentation
- Webhooks API - API endpoints for webhook management
- Pre-Processing Functions - Advanced JavaScript functions for EmailEngine
- List Webhook Routes API - API reference for listing routes
- Get Webhook Route API - API reference for route details